Working With Equations Help File
This equation allows you to find the energy of a moving object if its
mass and velocity are known.
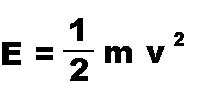
| VARIABLES: | E is Energy of the moving object |
(in Joules) |
| | m is Mass of the moving object |
(in kilograms) |
| | v is Velocity of the moving object |
(in meters per second) |
This equation allows you to find the scale height of a planet's
atmosphere if the temperature and composition of the atmosphere, and
the gravity of the planet is known.
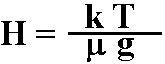
| VARIABLES: | H is the scale height of the atmosphere |
(in meters) |
| | k is the Boltzmann Constant | ( = 1.38 x 10
-23 Joules/Kelvin) |
| | T is the temperature of the atmosphere |
(in Kelvin) |
| |
μ is the
mean molecular weight of the gas |
(in kilograms) |
| | g is the gravity of the planet |
(in meters/second2) |
This equation allows you to find the amount of energy being emitted
per second by an object with a given size and temperature. The term in
parentheses is the surface area of a spherical object.
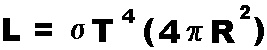
| VARIABLES: | L | is Luminosity of the
emitter |
(in Joules per second) |
| | σ | is the
Stefan-Boltzmann constant |
( = 5.67 x 10 -8) |
| | T | is Temperature of the emitter |
(in Kelvin) |
| | π |
is a constant | ( = 3.1415926) |
| | R |
is Radius of the emitter | (in meters) |
This equation allows you to find the amount of energy being received
per second by a square meter receiver from
an object with a given luminosity at a
given distance.
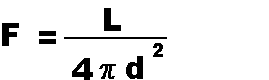
| VARIABLES:
| F | is Flux received |
(in Joules per second per square meter = Watts/meters2) |
| L | is Luminosity of the emitter |
(in Joules per second = Watts) |
| | π |
is a constant | ( =
3.1415926) |
| | d |
is Distance from the emitter | (in meters) |
This equation allows you to find the surface area of a sphere if its radius is known.
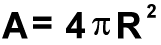
| VARIABLES:
| A | is Surface Area of sphere |
(in square meters) |
| π |
is a constant | ( =
3.1415926) |
| | R |
is Radius of sphere | (in meters) |
This equation allows you to find the escape velocity of an object if the mass and radius of the object are known.

| VARIABLES: | v is the Escape Velocity of an object |
(in meters/second) |
| | G is the Gravitational Constant | ( = 6.67 x 10
-11 meters3/(kilograms*seconds2)) |
| | M is the Mass of the object |
(in kilograms) |
| | R is the
Radius of the object |
(in meters) |
This equation allows you to find the surface gravity of an object if the mass and radius of the object are known.
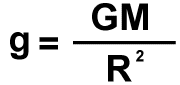
| VARIABLES: | g is the Surface Gravity of an object |
(in meters/second2) |
| | G is the Gravitational Constant | ( = 6.67 x 10
-11 meters3/(kilograms*seconds2)) |
| | M is the Mass of the object |
(in kilograms) |
| | R is the
Radius of the object |
(in meters) |
What can I do with these equations?
1. You Can Get a Relative Value for a Variable.
Some questions do not require knowing the actual values of any
variables! For example: "If the Earth's distance from the Sun were
doubled, how would the flux of sunlight to its surface change?"
- Step 1: First, decide whether the given change
will cause the given variable to increase or decrease. Common sense
tells us that moving the Earth farther away from the Sun will reduce
the amount of sunlight received, just as moving away from a hot fire
reduces the amount of heat received. Equation 4 tells us the same
thing mathematically: if we make the variable d
bigger, the denominator gets bigger, and the right hand side of Eq. 4
(the Flux) gets smaller.
- Step 2: Obtain a proportionality equation. In
our example d and F are changing
while all other quantities remain constant. To get a proportionality
equation, we drop everything out of Eq. 4 that remains constant. So
F is proportional to 1/d2.
- Step 3: Calculate the change quantitatively. In
this example, we are doubling (increasing by a factor of 2) the
variable d, so we plug in 2 for d,
square it, and find that F will go to 1/4 of its
original value. The final answer is that F will
decrease by a factor of 4 if the Earth's distance from the Sun is
doubled.
2. You Can Also Get an Absolute Numerical Value for a Variable.
If you know (or are given) the numerical values of all but one of the
variables in an equation, you can calculate the value of the final
variable. Let's use Equation 4 as an example to calculate how much
energy the Sun is emitting every second -- this is the Luminosity
(L) of the Sun. We know the value of
π (= 3.1415926), and we measure the
Flux of sunlight on a square meter of the Earth's surface (= 1387
Watts/meter2) and the Earth-Sun distance (= 1.496 *
1011 meters).
- Step 1: First, use algebra to manipulate the
equation so that the variable you are seeking appears by itself on the
one side of the equals sign. In our case, we multiply both sides of
Eq. 4 by the denominator 4πd2 to obtain
4πd2F =
L.
- Step 2: Next, substitute the numerical values
in for each of the known variables. In our case, we obtain:
(4)*(3.1415926)*(1.496 * 1011 meters)2 * (1387
Watts/meter2) = L.
- Step 3: Next, multiply the numbers together on a calculator while keeping track of the units. We find
3.9 * 1026 meters2 Watts/meters2 =
L.
- Step 4: Finally, simplify the units by cancelling out
common factors that appear both in the numerator and the denominator.
Our final answer for the luminosity of the Sun is 3.9 *
1026 Watts = L. Knowing that Luminosities
are measured in Watts provides a check that we have done the problem
correctly.
 Return to the
Working With Equations Page
Return to the
Working With Equations Page
Working With Equations written by Dr. Douglas P. Hamilton
Mike Asbury, and Amanda L. Proctor
 Return to the
Working With Equations Page
Return to the
Working With Equations Page 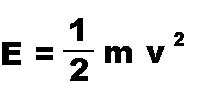
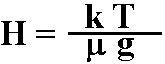
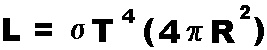
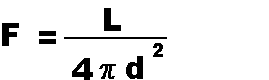
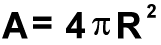

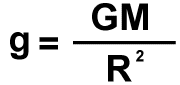
 Return to the
Working With Equations Page
Return to the
Working With Equations Page